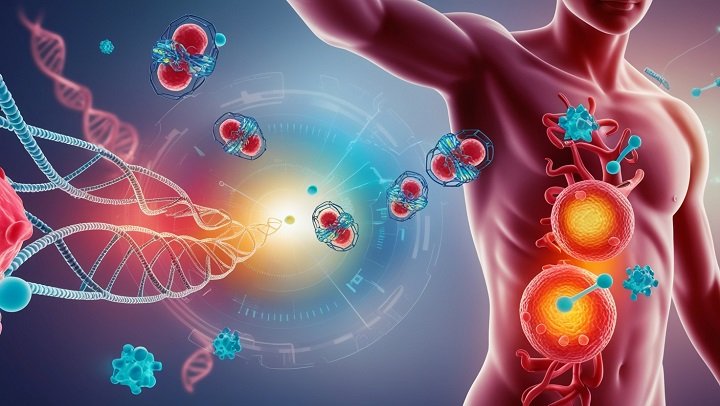
Nanotechnology in medication is a department of science that bargains with the control of matter on a nuclear or atomic scale, particularly at measurements between 1 and 100 nanometers. Envision being able to work with objects smaller than the width of a human hair—this is what nanotechnology does! Presently, when we apply this innovation to pharmaceuticals, we open up a world of conceivable outcomes that can alter the future of healthcare. From diagnosing illnesses before giving focused medications, nanotechnology in pharmaceuticals is revolutionizing how we approach ailments and healing.
What did you say? Is nanotechnology in drugs?
Maladies, like cancer, begin at the cellular level. Nanotechnology permits researchers to work specifically with these cells, settling issues some time ago that ended up being genuine issues. It’s like a superhero group working behind the scenes to save the day without anybody indeed noticing.
Why is Nanotechnology Critical in Medicine?
Early Illness Location: Conventional strategies of diagnosing infections like cancer frequently require the illness to develop expansive enough to be recognized by machines like MRI or CT. Nanotechnology may permit specialists to discover illnesses at the atomic level long before any symptoms appear.
Regenerative Pharmaceutical: Envision a world where harmed tissues and organs can be repaired, or indeed developed, from scratch. Nanotechnology is making progress in tissue building that might, sometime in the not-so-distant future, permit the regrowth of bones, skin, and other tissues.
1. tumor conduct
Cancer action is one of the most gifted ranges for nanotechnology in pharmaceuticals. One strategy includes utilizing nanoparticles to provide chemotherapy, especially to cancer cells These particles can be planned to target particular cells so they do not hurt sound tissues.
This makes medicines more viable while decreasing the obnoxious side impacts related to conventional cancer therapies.
Example: Gold nanoparticles are right now being investigated as a way to slaughter cancer cells. These particles can be infused into a patient’s circulatory system, where they collect in the tumor and are warmed by lasers, murdering the cancer cells without hurting the encompassing solid tissue.
2. Medicate Conveyance Systems
Nanotechnology is moving forward the way drugs are conveyed in the body. Conventional drugs spread all through the body, influencing both solid and undesirable cells. In any case, nanoparticles can be utilized to carry drugs to a particular area in the body, making medicines more viable and diminishing side effects.
For example, liposomes, which are minor circular vesicles, can carry cancer drugs straightforwardly to the tumor location. This focused on the medication conveyance framework, which progresses the adequacy of the treatment while decreasing the chance of harming solid cells.
3. Demonstrative Tools
Nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize how we analyze infections.
These sensors can recognize infection markers in blood tests or other liquids, giving an early caution framework for doctors.
High-Authority Connect: The National Cancer Institute is a driving specialist in the utilization of nanotechnology in cancer research. You can investigate their assets on nanotechnology and its part in early cancer locations here.
The Future of Nanotechnology in Medicine
The future of nanotechnology in medication looks unimaginably bright, with the potential to change the way we treat and oversee maladies. Here are a few future trends:
1. Personalized Medicine
One of the most energizing conceivable outcomes for nanotechnology is the improvement of personalized pharmaceuticals. This approach would tailor medications, particularly to an individual’s special hereditary cosmetics.
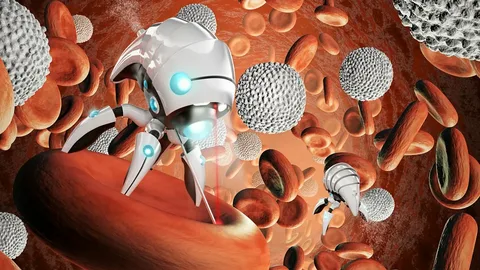
2. Nanobots
Even though they are still in early advancement, the potential for nanobots in medication is vast.
Whereas this innovation is still a work in advance, it holds extraordinary promise for the future of healthcare.
3. Tissue Regeneration
Nanotechnology seems moreover to play a critical part in tissue building and regenerative pharmaceuticals. Analysts are investigating ways to utilize nanomaterials to empower the development of unused tissues and organs. This innovation seems one day to permit us to recover harmed tissues or indeed make entire organs for transplant.
Challenges Confronting Nanotechnology in Medicine
1. Security Concerns

Nanoparticles are so small that they can pass through cell films and indeed into the circulatory system, which raises security concerns. Analysts are examining the long-term impacts of nanoparticles in the body to guarantee they do not cause unintended harm.
2. Fetching the Advancement of Nanotechnology in Medicine
3. Administrative Challenges
Guaranteeing the security and viability of nanotech medicines will require modern directions and oversight.
Conclusion:
Nanotechnology in medication is opening up unused wildernesses in healthcare. From prior illness discovery and more viable medications to the plausibility of personalized pharmaceuticals and tissue recovery, the potential for nanotechnology to alter the confines of pharmaceuticals is immense.
You can learn more about their assets here.
Nanotechnology is not just a buzzword in science; it’s a genuine, unmistakable innovation that’s, as of now, making a distinction. As inquiries proceed, the future of pharmaceuticals is likely to be smaller, more exact, and more personalized than ever before—thanks to nanotechnology.
Read More: