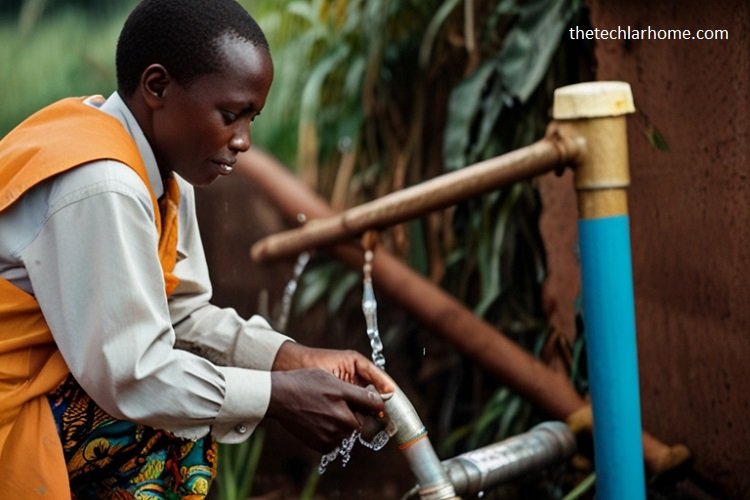
Water supply advancements of Uganda, a landlocked country in East Africa, are contributed to by basic water resources, tallying lakes, streams, and wetlands. In showing disdain toward this wealth, getting secure and clean water remains an essential challenge, particularly in common ranges. These proposals alter from routine procedures to progressed, creative courses of action pointed at moving forward to clean water across the country.
This article examines the differing water supply problems in Uganda, highlighting their ampleness, challenges, and influence on communities.
1. Layout of Water Resources in Uganda

Uganda is affluent in water resources, with major lakes like Lake Victoria, Lake Albert, and Lake Kyoga, and streams like the Nile gushing through its space. According to reports, around 38% of Ugandans still require access to secure drinking water, especially in more distant national zones. Urban ranges have a predominant scope, but undoubtedly there, the dispersal organization faces challenges like dejected systems and pollution.
The ask for strong water supply systems has driven the determination of a run of developments. These propels cater to unmistakable needs, from small natural communities to colossal urban populations.
2. Customary Water Supply Methods in Water Supply Advancements of Uganda
Before show day development, Ugandans developed an end to escalation on routine water sources like streams, conduits, hand-dug wells, cells, and water gathering. While these procedures are still in use, they are frequently dishonest and slanted to contamination. Key ordinary water supply methodologies include:
- Hand-dug Wells: These shallow wells are physically burrowed and are a common source of water in common ranges. In any case, they are helplessly drying amid dry spells and can easily. Get sullied by surface runoff, driving to waterborne diseases.
- Rainwater Collecting: In locales with tried and true precipitation, water gathering is a broadly practiced technique. Family units collect water utilizing direct systems like canals and capacity tanks. Though compelling in the stormy season, the technique is less strong amid dry periods.
These customary methodologies show disdain toward the truth that it is important to have obstructions in terms of versatility, water quality, and immovable quality. Inciting the requirement for more advanced water supply technologies.
3. Progressed Water Supply Progresses in Uganda
These advancements are more capable, temperate, and able to serve greater populations. A few of the key advancements include:
a. Boreholes and Hand Pumps of Water Supply Advancements of Uganda
courses of action in Uganda, particularly in common ranges. Boreholes are significant wells bored into the ground to get to underground aquifers. They are frequently fitted with hand pumps or motorized pumps to remove water.
- Advantages: Boreholes can grant a strong source of water without a drought of dry seasons. They are more regularly than not more significant than hand-dug wells. Reducing the danger of contamination.
- Challenges: Tall foundation costs and back prerequisites pose critical challenges. Too, boreholes in more distant locales habitually persevere from ignore and mechanical dissatisfactions due to a requirement of gifted technicians.
b. Gravity Stream Plans (GFS)
Gravity Stream Plans utilize a characteristic rise to transport water from a higher point. Such as a mountain spring. To lower-lying communities. This technique requires unimportant essentialness as water streams ordinarily do due to gravity.
- Advantages: GFSise is cost-effective and prudent, giving a ceaseless water supply with unimportant operational costs.
- Challenges: Actualizing GFS is location-dependent; it requires specific land conditions. In a few cases, long divisions and troublesome domains can complicate pipeline foundation and maintenance.
c. Solar-Powered Water Systems
Given Uganda’s satisfactory sunshine, solar-powered water systems have picked up ubiquity as a prudent course of action. These systems utilize sun-based sheets to control pumps that remove water from underground or surface sources. Solar-powered systems are especially effective in off-grid locales where control is unavailable.
- Advantages: Sun-based systems are very welcoming and have low operational costs once presented. They are particularly profitable in blocked-off ranges with confined infrastructure.
- Challenges: The tall beginning hypothesis and specialized aptitude required for foundation and upkeep can be boundaries to wide determination. Theft and vandalism of sun-situated sheets are also common issues in a few areas.
d. Channeled Water Supply Systems
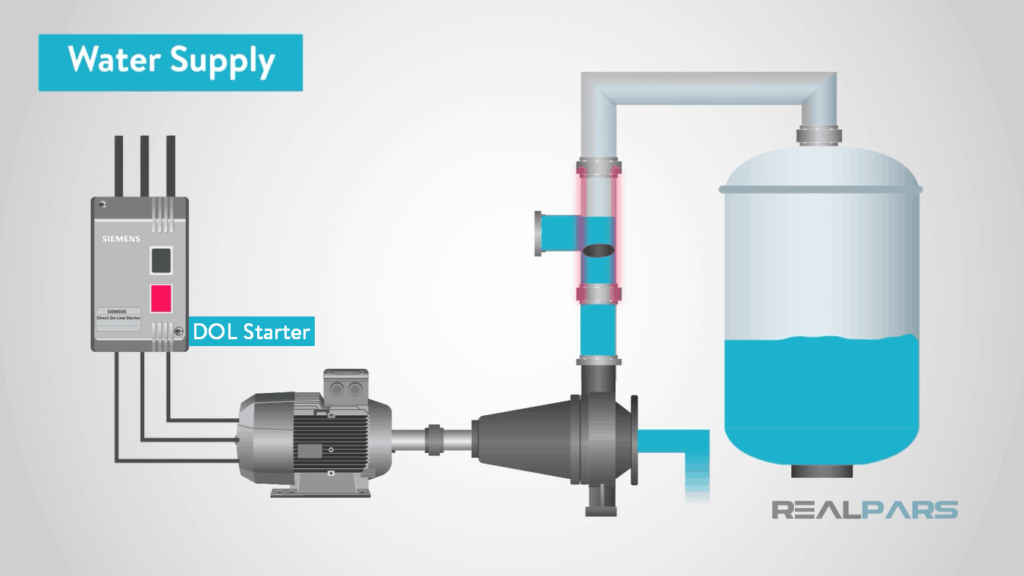
Piped water systems are common in urban and peri-urban locales. These systems incorporate the treatment and scattering of water through an organization of channels. Coming to families and educating. The National Water and Sewerage Venture (NWSC) is the fundamental substance tried and true for directing these systems in Uganda’s towns and cities.
- Advantages: Channeled systems offer strong and clean water clearly to homes. Diminishing the burden of water collection, especially for women and children.
- Challenges: The system required for channeled water systems is expensive, and organized expansions are frequently direct, taking off various peri-urban and common ranges underserved. Moreover, operationally inefficient viewpoints like spillages and illegal affiliations decrease the practicality of these systems.
a. Adroit Water Systems
Smart advancements are being facilitated in water organizations to overhaul efficiency and watching. These systems can be directed remotely, allowing. Expedient responses to issues like pipe bursts or pump failures.
- Advantages: Advanced efficiency, way better data organization, and diminished water mishaps are a few of the benefits. Quickly systematize well lock-in communities by giving them exact information on water utilization and costs.
- Challenges: Tall costs and the requirement for specialized know-how control the distance coming to the allotment of adroit water systems in Uganda. Particularly in natural areas.
b. Community-Managed Water Supply Systems
In various nation zones, community-based organization models have illustrated compellingly in keeping up water supply systems. Communities are arranged and empowered to supervise boreholes, pumps, and other water systems. Progressing proprietorship and sustainability.
- Advantages: Adjacent affiliation updates the back and convenience of water systems. It, in addition, develops community cohesion and ensures that the water supply meets neighborhood needs.
- Challenges: Keeping up with community organizations can be troublesome due to compelled budgetary resources. Require specialized capacities and potential clashes over water usage.
5. Challenges Going up against Water Supply Advancements in Uganda
Despite the development made, a few challenges destroy the practical execution and viability of water supply progress in Uganda:
- Technical Capacity: The triumph of cutting-edge water systems depends on the availability of a skilled workforce for foundation, operation, and upkeep. In various districts, the requirement for specialized expertise leads to dissatisfaction and abandonment.
- Environmental Components: Climate modification and characteristic degradation are impacting water sources. Post-dry season deforestation and defilement diminish water availability and quality, centering existing systems.
- Population Advancement and Urbanization: Fast mass improvement and urbanization are putting a huge weight on water supply systems. Expanding the system to meet rising demand is a relentless challenge, particularly in fast-growing urban areas.
- Governance and Course: Slight organization and an inadequate course lead to inefficient angles, corruption, and bungling of water resources and infrastructure.
6. The Portion of Government and NGOs in Making Strides Water Access
The government of Uganda, through workplaces like the Benefit of Water and Environment and the National Water and Sewerage Organization. Plays a central portion in water resource organization. These substances are available for approach specification, control, and the utilization of water supply wonders. The government, besides, collaborates with widespread organizations, NGOs, and private sector players to make strides in water access.
Several NGOs, such as WaterAid and the Uganda Water and Sanitation Organize (UWASNET), are viably included in executing water supply wonders. Supporting made strides in courses of action and giving specialized offer assistance. These collaborations have driven the compelling execution of a few community-based and large-scale water wonders across the country.
7. Conclusion: Towards Viable Water Supply Solutions
Uganda’s water supply advancements have progressed inside and out. Publicizing the belief that strides are being made to get clean water across the country. Be that as it may, challenges like subsidizing capacity and common components must be addressed to ensure attainable courses of action. By leveraging both routine and cutting-edge progress and developing community intrigue and government commitment, Uganda can continue to make progress toward broad access to secure and reliable water.
The travel toward prudent water supply in Uganda is advancing, requiring nonstop progression of hypotheses and collaboration among all accomplices.